本文目录
背景
今天QQ群中CodeCook问了个问题,在PowerShell Studio 2012 工程中创建了一个project,包含了两个窗体,一个主窗体,一个子窗体。在主窗体的按钮单击事件中,启动子窗体。这用c#在vs环境下实现,估计一分钟就够了;在PowerShell ISE下,脚本写得再溜,也得十一二分钟吧。在PowerShell Studio 2012中用一分钟也就够了,这也算体现了PowerShell Studio 2012的价值了。
PowerShell Studio 是什么
PowerShell Studio是一套基于PowerShell的包含脚本编辑,脚本调试,Windows Form设计等功能的集成开发环境(IDE)。其最大的亮点是支持拖拽控件式的Windows Form设计。
PowerShell Studio的调用原理
理解了这个问题,纠结CodeCook的问题自然迎刃而解。
fprojs工程文件
PowerShell Studio的工程文件后缀名为:fprojs 。文件内容自然包含了整个工程的文件清单:
<ProjectState>
<Version>1.0</Version>
<FileID>fc295821-bae7-4898-a6c5-bb545f8a1bf4</FileID>
<OpenFiles>
<File>Globals.ps1</File>
<File>Startup.pfs</File>
<File>MainForm.pff</File>
<File>child.pff</File>
</OpenFiles>
</ProjectState>
Globals.ps1文件
Globals.ps1文件为一个原汁原味的PowerShell脚本文件,内面定义一些全局变量或者函数。
Startup.pfs文件
Startup.pfs为工程文件的入口,类似C#中的main函数。默认内容为:
function Main {
Param ([String]$Commandline)
if((Call-MainForm_pff) -eq "OK")
{
}
$global:ExitCode = 0 #Set the exit code for the Packager
}
其中关键一行Call-MainForm_pff,用来调用启动主窗体,格式为Call-【窗体名】_pff,这也是本篇博文的灵魂。那也就是意味着在接下的按钮的click事件中我是不是可以这样 Call-ChildForm_pff 调用子窗体,是的,完全正确。
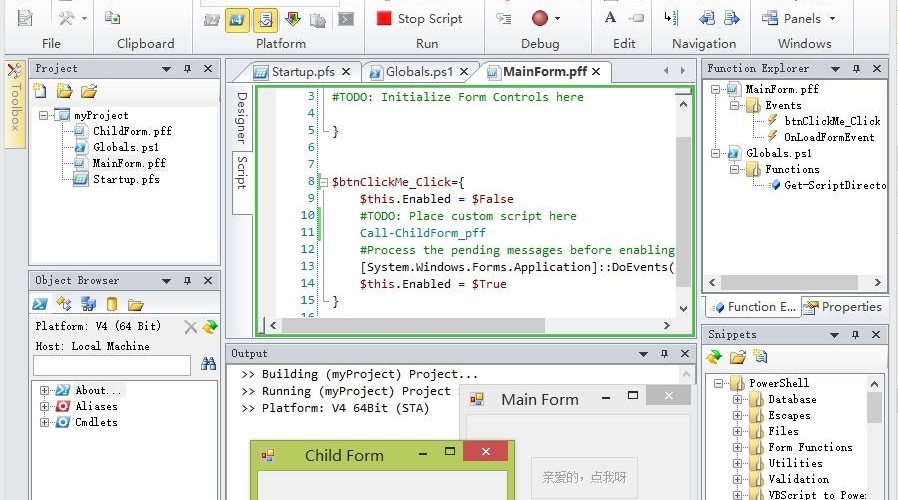
但是CodeCook犯了个小错误,直接F5运行,一直提示有错误。为什么,因为F5是运行当前脚本文件,而这种pff文件是一个伪脚本,不是原汁原味的PowerShell脚本文件,所以报错。应当使用Ctrl+F4运行整个工程。效果如下:
Form.pff文件
那我们再看看pff的文件结构,结构非常清晰,甚至比visual studio自动生成的文件design.cs还清晰(有过之,而无不及),前面使用xml定义控件。
<Object type="System.Windows.Forms.Form, System.Windows.Forms, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" name="MainForm" children="Controls">
<Property name="ClientSize">223, 122</Property>
<Property name="Name">MainForm</Property>
<Property name="StartPosition">CenterScreen</Property>
<Property name="Text">Main Form</Property>
<Event name="Load">OnLoadFormEvent</Event>
<Object type="System.Windows.Forms.Button, System.Windows.Forms, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" name="btnClickMe" children="Controls">
<Property name="Location">63, 41</Property>
<Property name="Name">btnClickMe</Property>
<Property name="Size">109, 44</Property>
<Property name="TabIndex">1</Property>
<Property name="Text">亲爱的,点我呀</Property>
<Property name="UseVisualStyleBackColor">True</Property>
<Event name="Click">btnClickMe_Click</Event>
</Object>
</Object>
紧接着,利用CDATA定义控件对应的事件:
<Code><![CDATA[
$OnLoadFormEvent={
#TODO: Initialize Form Controls here
}
$btnClickMe_Click={
$this.Enabled = $False
#TODO: Place custom script here
Call-ChildForm_pff
#Process the pending messages before enabling the button
[System.Windows.Forms.Application]::DoEvents()
$this.Enabled = $True
}
]]></Code>
最后定义引用和版本信息等:
<Assemblies>
<Assembly>System.Management.Automation, Version=3.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35</Assembly>
<Assembly>System, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089</Assembly>
</Assemblies>
用小学老师作文评语来评价就是:”层次分明,脉络清晰”
导出为一个独立的PowerShell脚本
不管过程怎么花哨,最终得回归到一个Powershell脚本文件,这才是PowerShell Studio的真正归宿。导出后的ps1文件中包含了每个工程文件的名称和源文件的加密数据:
#region Source: Startup.pfs
#region File Recovery Data (DO NOT MODIFY)
<#RecoveryData:
CwcAAB+LCAAAAAAABAC9Vdtu2zAMfR+wf/AHZJY9x0kLqAYCBx2KYVtQF9teFYVOhcqSoUsD//2U
zNfY6YY+BH4xDy+HokQSPwKVr6CqNTEk+fjB8/APxfZMEH7POHwnBSSZIcrY0i9zjdFIe/I5Sj9B
aSZFEvqfMeoDJ4uV1lBsOQN9kjukSrJKGyj8b0SQPRQgjL+yRhbEOOeZV0e5i/zg+M281HJjFdwJ
sEYRPvM21sWlX6F6ki/gDMNtHt3EC7KLFnOIYoxapmnmjmP+vxzb5ZLENF6Et9Ecgpvbf3L4v5jY
yYP276Uq9FUY14ocmNi/hyuI8jhf5mG4iwMSkTe4Ck2l4mx7nRO5N3oVot8Fv86BmAJqpKoyUK+M
wrsextuX1YpN5+ENoS+u0VST1BcQ4ALXYmfQdvcJRJNoDT7Qus0HpkPUtTfLQZtUwamzkxCjEdZa
p1a7EdDoe7EvKTacmNz1VvLJxW2FVv1oRfa0SgKM6r/OUR5AZc/AeTOv3Pgag3Wx0LBaOANqFTOV
hxpk6HA2G7tzTKIbJXeWmrH1JUWNn1/VFLoGTRUrh2VGk2gqi5KIql/1cySVZeU2wfPgasbYgzCg
3LY4S3Aanlwtfx0uq1xmx5UxzLWHYDRYQ6j3+t1b6C+/P5RBcLgLBwAA#>
#endregion
#----------------------------------------------
#region Import Assemblies
#----------------------------------------------
[void][Reflection.Assembly]::Load("System, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089")
[void][Reflection.Assembly]::Load("System.Windows.Forms, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089")
[void][Reflection.Assembly]::Load("System.Drawing, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a")
[void][Reflection.Assembly]::Load("mscorlib, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089")
[void][Reflection.Assembly]::Load("System.Data, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089")
[void][Reflection.Assembly]::Load("System.Xml, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089")
[void][Reflection.Assembly]::Load("System.DirectoryServices, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a")
#endregion Import Assemblies
我们看看之前提到的Call-ChildForm_pff变成什么样子了,贴出一段,这下很眼熟了吧。
#---------------------------------------------- #region Generated Form Objects #---------------------------------------------- [System.Windows.Forms.Application]::EnableVisualStyles() $formChildForm = New-Object 'System.Windows.Forms.Form' $InitialFormWindowState = New-Object 'System.Windows.Forms.FormWindowState' #endregion Generated Form Objects #…… #region Generated Form Code #---------------------------------------------- # # formChildForm # $formChildForm.ClientSize = '249, 109' $formChildForm.Name = "formChildForm" $formChildForm.Text = "Child Form" $formChildForm.add_Load($formChildForm_Load) #endregion Generated Form Code #---------------------------------------------- #Save the initial state of the form $InitialFormWindowState = $formChildForm.WindowState #Init the OnLoad event to correct the initial state of the form $formChildForm.add_Load($Form_StateCorrection_Load) #Clean up the control events $formChildForm.add_FormClosed($Form_Cleanup_FormClosed) #Store the control values when form is closing $formChildForm.add_Closing($Form_StoreValues_Closing) #Show the Form return $formChildForm.ShowDialog()
写作最后
PowerShell Studio像PowerShell一样,其方便成就了其强大,可以用来做一些小的Windows窗体工具。但是考虑到PowerShell解释性语言的性能,你会用它做软件吗?反正我是不会。
请尊重原作者和编辑的辛勤劳动,欢迎转载,并注明出处!

哇,我出名了诶!
所以,还要感谢你啦。